
We offer a full line of cardiac and coronary CT, MRI, and nuclear medicine imaging. Our state-of-the-art Toshiba 320 slice CT scanner and 3T Siemens Skyra MRI magnet allows us to perform studies to assess coronaries and the aortic valve for percutaneous replacement.
Cardiac computed tomography or cardiac CT, is a painless test that uses an x-ray machine to take clear, detailed pictures of the heart. Doctors use this test to look for heart problems.
During a cardiac CT scan, an x-ray machine will move around your body in a circle. The machine will take a picture of each part of your heart. A computer will put the pictures together to make a three-dimensional picture of the whole heart.
Sometimes an iodine-based dye (contrast dye) is injected into one of your veins during the scan. The contrast dye highlights your coronary arteries on the x-ray pictures. This type of CT scan is called a coronary CT angiography or CTA.
Provided by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
For additional Information, visit radiologyinfo.org - Cardiac (Health) Screening
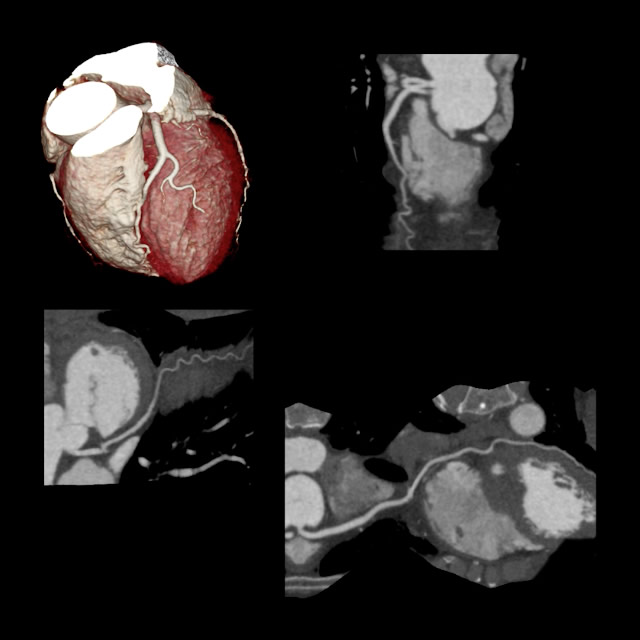
Cardiac CT
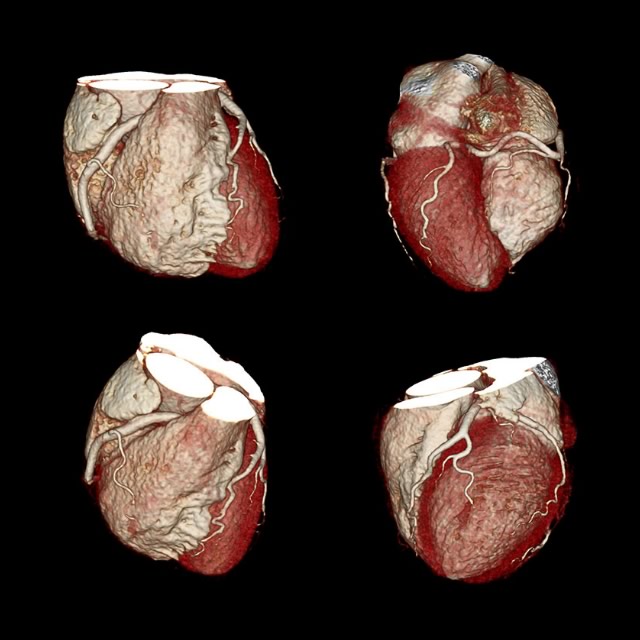
Cardiac CT
Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, is a non-invasive imaging technology that produces three dimensional detailed anatomical images without the use of damaging radiation. It is often used for disease detection, diagnosis, and treatment monitoring. It is based on sophisticated technology that excites and detects the change in the direction of the rotational axis of protons found in the water that makes up living tissues.
Cardiac MRI creates both still and moving pictures of your heart and major blood vessels. Doctors use cardiac MRI to get pictures of the beating heart and to look at its structure and function. These pictures can help them decide the best way to treat people who have heart problems.
MAGNETOM Skyra
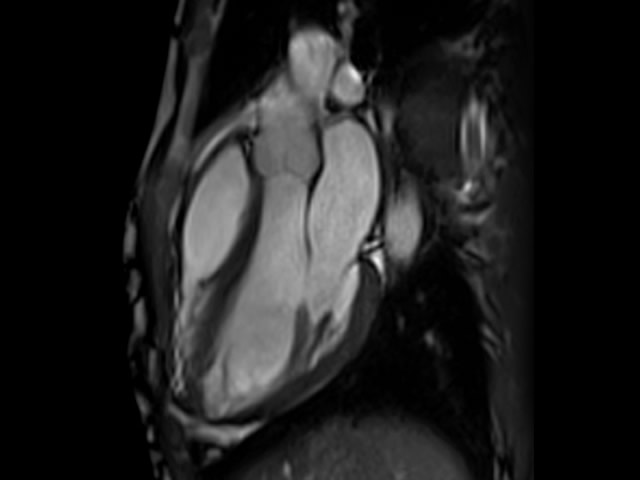
Cardiac MRI
Provided by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
For additional information, visit radiologyinfo.org - Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Cardiac (Heart)
Siemens Biograph TruePoint PET/CT
Our nuclear medicine services include a variety of advanced imaging modalities used to assess bodily functions and to diagnose and treat disease. Some examples include single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) to diagnose and track the progression of heart disease, positron emission tomography (PET) to detect cancer and monitor its progression, and DaTscan to aid in the assessment and diagnosis of patients in whom a parkinsonian syndrome or essential tremor is suspected.
For Cardiac Nuclear Medicine information, visit radiologyinfo.org - Cardiac Nuclear Medicine